


Next: Curriculum Vitae
Up: disshtml
Previous: Abbreviations and Symbols
Contents
-
- 1
- Austrian Academy of Sciences, Institute of High Energy Physics, Nikolsdorfergasse 18,
A-1050 Vienna, Austria (http://wwwhephy.oeaw.ac.at)
- 2
- European Laboratory for Particle Physics, CH-1211 Geneva 23,
Switzerland
(http://www.cern.ch)
- 3
- Particle Data Group, Particle Physics Booklet,
Springer, July 2000
(http://pdg.lbl.gov)
- 4
- S.Cittolin, Introduction to CMS, CMS Brochure, March 1988
(http://cmsinfo.cern.ch/Brochures/IntroToCMS.pdf)
- 5
- C.E.Wulz (CMS Collaboration), CMS - Concept and Physics Potential,
CMS CR-1999/012, March 1999
(http://cmsdoc.cern.ch/cgi-doc/Grep/documents/all.html?_GEN_)
- 6
- T.S.Virdee (CMS Collaboration), The CMS Experiment at the LHC,
CMS CR-1998/025, January 1999
(http://cmsdoc.cern.ch/cgi-doc/Grep/documents/all.html?_GEN_)
- 7
- CMS Collaboration, CMS Tracker Technical Design Report, CERN/LHCC
98-6, April 1998 (http://cmsdoc.cern.ch/cms/TDR/TRACKER/tracker.html)
- 8
- CMS Collaboration, Addendum to the CMS Tracker TDR, CERN/LHCC 2000-016,
February 2000 (http://cmsdoc.cern.ch/cms/TDR/TRACKER/tracker_addendum.pdf)
- 9
- M.Winkler, dE/dx in Halbleiterdetektoren,
Diploma Thesis, Vienna University of Technology, September 1998
- 10
- L.D.Landau, On the Energy Loss of Fast Particles by Ionization,
Collected Papers of L.D.Landau, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1965
- 11
- C.Ede, Messung der Energiedeposition von geladenen
Teilchen in dünnen Siliziumdetektoren,
Diploma Thesis, Vienna University of Technology, December 1999
- 12
- M.Friedl, PSI-Testbeam December 2000 (http://cern.ch/friedl
 PSI-Testbeam)
PSI-Testbeam)
- 13
- P. Shulek et al., Fluctuations of Ionization Losses
Soviet Journal of Nuclear Physics 4 (1967), 400
- 14
- M.S.Tyagi, Introduction to Semiconductor Materials and Devices,
John Wiley & Sons, 1991
- 15
- S.M.Sze, Semiconductor Devices, John Wiley & Sons, 1985
- 16
- S.Ramo, Currents Induced by Electron Motion,
Proceedings of the I.R.E. 27 (1939), 584-585
- 17
- CERN RD42 Collaboration - Diamond Detectors (http://cern.ch/rd42)
- 18
- CERN RD8 Collaboration - GaAs Detectors (http://ppewww.ph.gla.ac.uk/RD8)
- 19
- M.Friedl, T.Bauer, M.Krammer, A Simple Model of Charge
Collection in Silicon Detectors,
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 461 (2001), 192-196
- 20
- T.Bauer, M.Friedl, Silicon Detector Simulation (http://cern.ch/bauer/sim)
- 21
- Tabularized NIEL values compiled from several publications
are available at
http://sesam.desy.de/~gunnar
- 22
- Rose Collaboration (RD48), Third RD48 Status Report, CERN/LHCC 2000-009,
December 1999 (http://cern.ch/rd48)
- 23
- H.Pernegger, The Silicon Ministrip Detector of the DELPHI Very Forward
Tracker, PhD Thesis, Vienna University of Technology, February 1996
- 24
- G.Baricchello et al., Performance of Long Modules
of Silicon Microstrip Detectors, CERN-PPE 97-162, December 1997
(http://nomadinfo.cern.ch/Public/detect/star/publications.html)
- 25
- S.Braibant et al., Investigation of design parameters and choice
of substrate resistivity and crystal orientation for the CMS silicon microstrip
detector, CMS NOTE 2000/056 (http://cmsdoc.cern.ch/documents/00/note00_011.pdf)
- 26
- H.Pernegger (PHOBOS Collaboration), Layout and
tests of silicon pad detectors for the PHOBOS experiment at RHIC,
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 419 (1998), 549-555
- 27
- B.Back et al., The PHOBOS Silicon Pad Sensors,
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 447 (2000), 257-263
- 28
- Y.Gornushkin et al., Monolithic Active Pixel Sensors for Charged
Particle Tracking, 9th Vienna Conference on Instrumentation, Vienna, A,
February 2001 (http://wwwhephy.oeaw.ac.at/u3w/w/wcc/www/talks/Thursday/Dulinski.pdf)
- 29
- W.de Boer et al., Lorentz angle measurements in irradiated silicon
detectors between
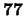 and
and 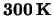 ,
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 461 (2001), 200-203
,
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 461 (2001), 200-203
- 30
- A.Rudge, Comparison of Charge Collection in Semiconductor
Detectors and Timing Resolution, Using a Sub-Nanosecond Transimpedance
Amplifier, Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 360 (1995), 169-176
- 31
- E. Nygård et al., CMOS Low
Noise Amplifier for Microstrip Readout: Design and Results,
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 301 (1991), 506-516
- 32
- S.Gadomski et al., The Deconvolution Method of Fast Pulse
Shaping at Hadron Colliders,
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 320 (1992), 217-227
- 33
- N.Bingefors et al., A novel technique for fast pulse-shaping
using a slow amplifier at LHC,
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 326 (1993), 112-119
- 34
- J.D.Schipper, Low-Noise Preamplifier (http://www.nikhef.nl/~jds/vlsi)
- 35
- M.Raymond et al., Measurements of transistors and silicon
microstrip detector readout circuits in the Harris AVLSIRA rad-hard CMOS process,
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 351 (1994), 449-459
- 36
- TEMIC Semiconductors, MHS S.A., La Chantrerie - Route de Gachet, B.P. 70602,
F-44306 Nantes Cedex 3, France (http://www.temic-semi.com)
- 37
- Information on the IBM
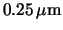 process can be found at
http://www.chips.ibm.com/services/foundry/offerings/cmos/6sf
process can be found at
http://www.chips.ibm.com/services/foundry/offerings/cmos/6sf
- 38
- A.Duccio, The Tracker Layout (http://cern.ch/duccio/layout/whole.html)
- 39
- R.Baur, W.Bertl, The CMS Pixel Vertex Detector,
Nuclear Physics B, Proc. Suppl.: 78 (1999), 293-300
- 40
- K.Gabathuler, CMS Pixel Readout Electronics, International Pixel
Detector Workshop - Pixel 98, Batavia, IL, USA, FERMILAB-Conf-98-196,
171-178 (http://fnalpubs.fnal.gov/archive/1998/conf/Conf-98-196.html)
- 41
- R.Baur, Readout Architecture of the CMS Pixel Detector,
International Pixel Detector Workshop - Pixel 2000, Genova, Italy,
submitted to Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A
- 42
- Supply of Silicon Micro-Strip Sensors for The CMS Silicon Strip Tracker
(SST), Invitation to Tender/Technical Specification, CERN/IT-2777/EP/CMS,
October 2000 (http://cern.ch/angarano/sensors/specifications.pdf)
- 43
- M.Lenzi (CMS Tracker Collaboration), Performance of the
all-silicon CMS Tracker, November 2000, submitted to
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A
- 44
- R.Wedenig (CMS Tracker Collaboration), Assembly Studies for
Silicon Detector Modules, 9th Vienna Conference on Instrumentation,
Vienna, A, February 2001 (submitted to Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A)
- 45
- Information on the Philips
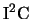 bus (including specifications) can be found at http://www.semiconductors.philips.com/i2c
bus (including specifications) can be found at http://www.semiconductors.philips.com/i2c
- 46
- M.Raymond, APV25-S0 Analogue Test Results, December 1999 (available
at http://www.te.rl.ac.uk/med/apv25_web/APV25_talk.pdf)
- 47
- M.Raymond et al., The APV6 Readout Chip for CMS Microstrip Detectors,
CERN/LHCC 97-60, September 1997
(http://www.te.rl.ac.uk/med/apv6/papers/leb_apv6_london97_paper.pdf)
- 48
- R.Turchetta et al., Design and results from the APV25,
a Deep Submicron CMOS Front-End Chip for the CMS Tracker, 4th International Symposium on
Development and Application of Semiconductor Tracking Detectors, Hiroshima, Japan,
March 2000
(http://www.te.rl.ac.uk/med/apv25_web/hiroshima00_slides.pdf)
- 49
- L.L.Jones et al., The APV25 Deep Submicron Chip for CMS
Detectors, CERN/LHCC 99-09, p.162-166, September 1999
(http://www.te.rl.ac.uk/med/apv25_web/leb99_paper.pdf)
- 50
- G.Marseguerra, Prestazioni del chip di lettura APV25 dei rivelatori
a microstrip su silicio del tracker di CMS, PhD Thesis, July 2000
(http://pcigor2.pd.infn.it/APV_25/giorgio/Main.ps.gz)
- 51
- Information and Manuals of the Microelectronics Design Group, Instrumentation
Department, Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, are available at http://www.te.rl.ac.uk/med
- 52
- Z.Y.Chang, W.M.C.Sansen, Low-Noise Wide Band Amplifiers in
Bipolar and CMOS Technologies, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, November 1990
- 53
- A.Neviani, APV25S0 - Calibration Circuit
(http://www.te.rl.ac.uk/med/apv25_web/cal.pdf)
- 54
- CMS Tracker Control (http://pcvlsi5.cern.ch/CMSTControl)
- 55
- G.Cervelli et al., Radiation Tolerant
Linear Laser Driver IC
(http://cern.ch/cms-tk-opto/technical.html)
- 56
- F.Faccio et al., An 80Mbit/s radiation tolerant Optical Receiver
for the CMS digital optical link (http://cern.ch/cms-tk-opto/dev_pubs.html)
- 57
- T.Bauer, Digital Optical Link (http://cern.ch/bauer/opto.html)
- 58
- CERN RD12 Collaboration - Timing, Trigger and Control (TTC) Systems for LHC
Detectors (http://cern.ch/TTC/intro.html)
- 59
- J.Coughlan, The CMS Tracker Front-End Driver (FED)
(http://hepwww.rl.ac.uk/cms_fed)
- 60
- Information about the cooling box developed at HEPHY and the MultiTherm temperature
monitoring system can be found at http://cern.ch/friedl
- 61
- ROOT - An Object-Oriented Data Analysis Framework (http://root.cern.ch)
- 62
- M.Friedl, APV6 Vienna Manual (http://cern.ch/friedl
 APV6)
APV6)
- 63
- W.Adam et al., Response of a silicon detector to protons and
pions with momenta of 270, 310 and 405 MeV/c,
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 441 (2000), 427-437
- 64
- M.Raymond et al., The CMS Tracker APV25
 CMOS Readout Chip, CERN/LHCC 2000-41, p.130-134,
September 2000 (http://cern.ch/lebwshop/LEB00_Book/tracker/raymond.pdf)
CMOS Readout Chip, CERN/LHCC 2000-41, p.130-134,
September 2000 (http://cern.ch/lebwshop/LEB00_Book/tracker/raymond.pdf)
- 65
- Paul Scherrer Institute, CH-5232 Villigen, Switzerland (http://www.psi.ch)
- 66
- J.Fulcher et al., Single Event Upset Studies on the APV25 Front
End Readout Chip, CERN/LHCC 2000-41, p.260-264, September 2000 (http://cern.ch/lebwshop/LEB00_Book/rad/fulcher.pdf)
- 67
- M.Friedl, Strasbourg FE Hybrid Test (http://cern.ch/friedl
 APV25)
APV25)
- 68
- Vienna University, Institute of Material Physics, High Temperature Superconductivity
Group, Kopernikusgasse 15, A-1060 Vienna, Austria (http://www.univie.ac.at/materialphysik)
- 69
- F.Vasey et al., CMS Tracker Optical Readout Link Specification,
Part 1: Analog Readout System (http://cern.ch/cms-tk-opto/specifications.html)
- 70
- T.Bauer, F.Vasey, A model for the CMS tracker analog optical link,
CMS NOTE 2000/056 (http://cern.ch/cms-tk-opto/perf_pubs.html)
- 71
- T.Bauer, M.Friedl, Optical Link Evaluation (http://cern.ch/friedl
 AOL)
AOL)
- 72
- F.Vasey et al., CMS Tracker Optical Links (http://cern.ch/cms-tk-opto)
- 73
- M.Friedl, Analog Performance of the FED-PMC (http://cern.ch/friedl
 FED)
FED)
- 74
- Tektronix Technique Primer 47W-7209, Sampling Oscilloscope
Techniques
(http://www.tektronix.com/Measurement/App_Notes/sampling_primer)
- 75
- Imperial College, High Energy Physics, Silicon Group, Blackett Laboratory,
Prince Consort Road, London SW7 2BZ, United Kingdom (http://www.hep.ph.ic.ac.uk/silicon)
Markus Friedl
2001-07-14